Figure 5: Myxosarcoma in 20-month-old male rat (D’Lochlan).
Case history and photos
History
A 20-month-old, 672 g, intact, standard Dalmatian male rat with no previous history of illness.
Clinical Signs
Mass noted on the cervical area of the neck.
Diagnosis
Tumor
Treatment
Surgery was performed on two separate occasions to debulk the tumor. The debulking of the tumor consisted, basically, of the scooping out of diseased tissue. The space that was left in the debulked tumor would then fill with blood and serous fluid.
D’Lochlan was placed on Baytril, as a prophylaxis to prevent infection, and given Banamine for mild post-op pain.
Due to the presentation of the tumor it was not known until after death that it was fully encapsulated and able to be excised.
Outcome
Euthanasia was required due to the rapid growth and malignancy of the tumor precluding quality of life.
Follow-up
NECROPSY:
The necropsy was performed immediately after euthanasia. A large encapsulated left lateral cervical mass with salivary gland attachment was noted.
HISTOPATHOLOGY:
(Section of debulked tumor)
SUMMARY
The sections of tissue evaluated showed an undifferentiated sarcoma with features of a myxosarcoma from the salivary gland. The history of rapid growth of the mass along with the lack of distinct borders suggests this a malignant tumor with a good possibility of recurrence.
Tissue Masses: Several pieces of tissue from a debulked mass were evaluated histologically. One small area of one of the pieces of tissue contained a few clusters of serous cells forming acinar type structures (salivary gland). The majority of the tissue is composed of solid sheets of pleiomorphic, predominantly spindleoid, cells with scant cytoplasm, round to oval vesicular nuclei with rare mitotic figures. Cells are separated by abundant lacey, faintly basophilic, stroma; neoplastic cells extend to all borders of the evaluated tissue. Undifferentiated sarcoma, possibly myxosarcoma.
Photos
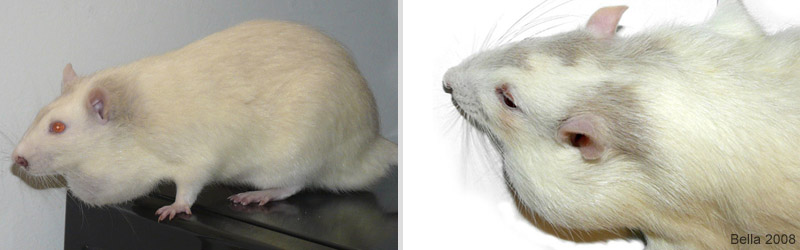 The photo to the left shows D’Lochlan a few days before euthanasia. The stress from his condition is apparent by the porphyrin discharge from his eyes and nose. The second photo was taken before the necropsy. |
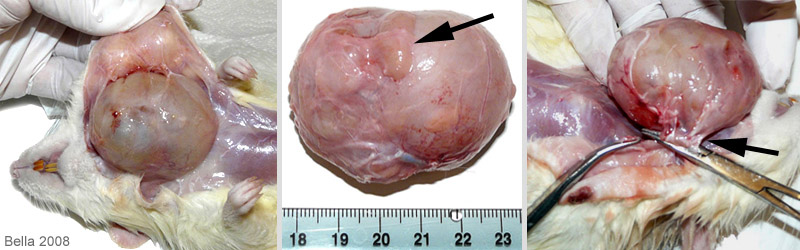 During the necropsy it was apparent that the mass was well encapsulated. In the middle photo the black arrow is pointing to salivary gland tissue. The third photo shows the area of attachment which includes connective tissue as well as the tumor’s blood supply vessel. |
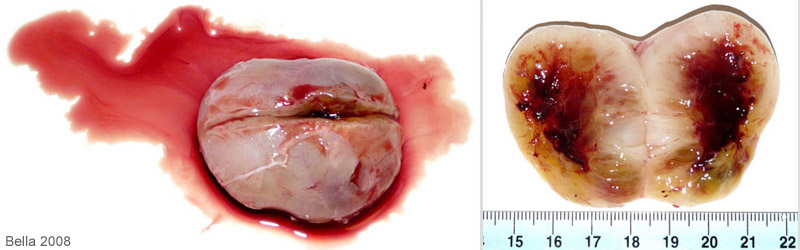 When the mass was bisected serosanguineous fluid (serum mixed with blood) drained from it. In the second photo you can see the area of the tumor that had been “scooped out” during the two debulking surgeries. It is not unusual for the body to try to fill up the empty space left after a tumor removal or debulking with blood and/or fluid.. |
Surgeon- R. Mackinnis, D.V.M. South Seminole Animal Hospital (FL)
Histopathology by IDEXX RADIL (University of Missouri)
Pathologist- Glenn Jackson, D.V.M.
Necropsy and photos by Joanne “Bella” Hodges


